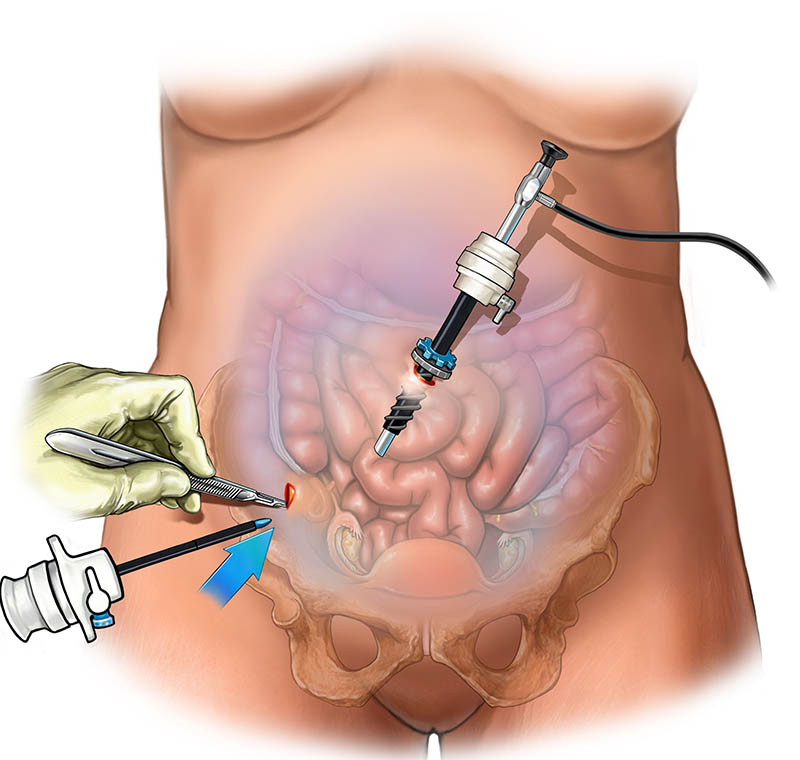
Keyhole surgery is a type of surgery in which the surgeon uses only small cuts to get through the skin. It requires special training. People who have keyhole surgery usually recover quite quickly.
Laparoscopy is keyhole surgery used to examine or operate on the interior of the abdominal or pelvic cavities. It is performed under general anaesthesia, usually by a surgeon or gynaecologist (women’s health specialist).
During laparoscopy a small cut is made in the abdomen. A thin tube containing a light and camera, known as a laparoscope, is then inserted to look inside the abdomen and pelvis. Gas is used to inflate the belly so the surgeon can see the organs properly.
One or more other small cuts may be made for other small instruments if needed.
Laparoscopy is used to diagnosis conditions or perform surgery in the abdominal and pelvic area. It can be used to:
- assess painful or heavy periods
- remove the uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries
- diagnose or treat endometriosis
- diagnose or remove ovarian cysts and tumours
- assess female infertility
- treat ectopic pregnancy
- remove the gall bladder or parts of the intestine
- take a biopsy (a small tissue sample) for testing
- search for the causes of abdominal or pelvic pain