What is ICSI?
- ICSI is an acronym for Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection.
- A fancy way of saying “inject sperm into egg”
- ICSI is a very effective method to fertilize eggs in the IVF lab after they have been aspirated from the female
Its main use is for significant male infertility cases in normal IVF, many sperm are placed together with an egg, in hopes that one of the sperm will enter and fertilize the egg. With ICSI, the embryologist takes a single sperm and injects it directly into an egg.
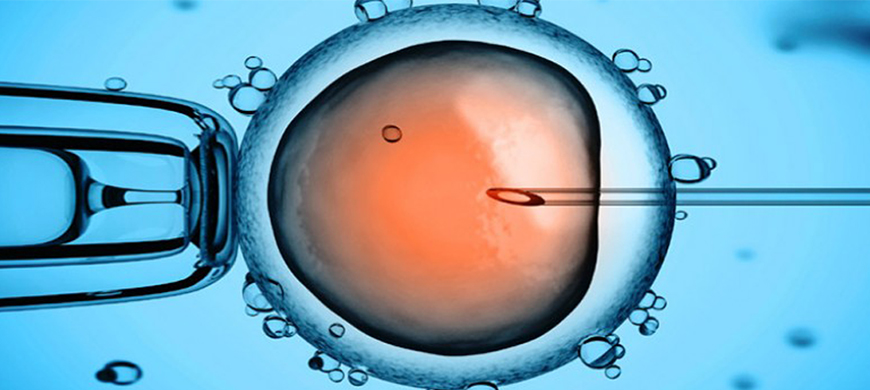
Why is ICSI Done?
ICSI is typically used in cases of severe male infertility, including:
- Sperm concentrations of less than 15-20 million per milliliter
- Low sperm motility – less than 35%
- Very poor sperm morphology (subjective – specific cutoff value is debatable)
- Having previous IVF with no fertilization – or a low rate of fertilization (low percentage of mature eggs that were normally fertilized).
- If a man does not have any sperm in his ejaculate, but he is producing sperm, they may be retrieved through testicular sperm extraction, or TESE. Sperm retrieved through TESE require the use of ICSI.
- ICSI is also used in cases of retrograde ejaculation, if the sperm are retrieved from the man’s urine.
- ICSI may also be done if regular IVF treatment cycles have not achieved fertilization.
- Sometimes it is used for couples that have a low yield of eggs at egg retrieval. In this scenario, ICSI is being used to try to get a higher percentage of eggs fertilized than with conventional insemination of the eggs (mixing eggs and sperm together).
